High mobility group box 1 protein, also known as high-mobility group protein 1 (HMG-1) and amphoterin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HMGB1 gene. HMGB1 is a multifunctional protein with various roles in different cellular compartments. It is associated with various pathogenesis such as cancers, neurodegenerative disorders, and multiple inflammatory diseases. HMGB1 has attracted the attention of both basic and clinical researchers as HMGB1 is a therapeutic target for a wide range of diseases. Arigo offers a total solution to facilitate the HMGB1-related research.
Nuclear and cytosolic HMGB1
In the nucleus, HMGB1 acts as a DNA-binding protein for gene transcription, gene regulation and DNA repair. In the cytosol, HMGB1 induces autophagy by interacting with Beclin-1 which results in its dissociation from Bcl2 and the subsequent induction of autophagy.
Extracellular HMGB1
In the extracellular compartment, HMGB1 is passively released by necrotic cells and acts as a chemokine and DAMP (Damage-associated molecular pattern) to trigger inflammatory responses. Besides, HMGB1 is also secreted from activated dendritic cells and macrophages and functions as a cytokine, it acts as a ligand for RAGE, TLR-2 and TLR-4 thus activating the signal pathways and the following inflammation responses.
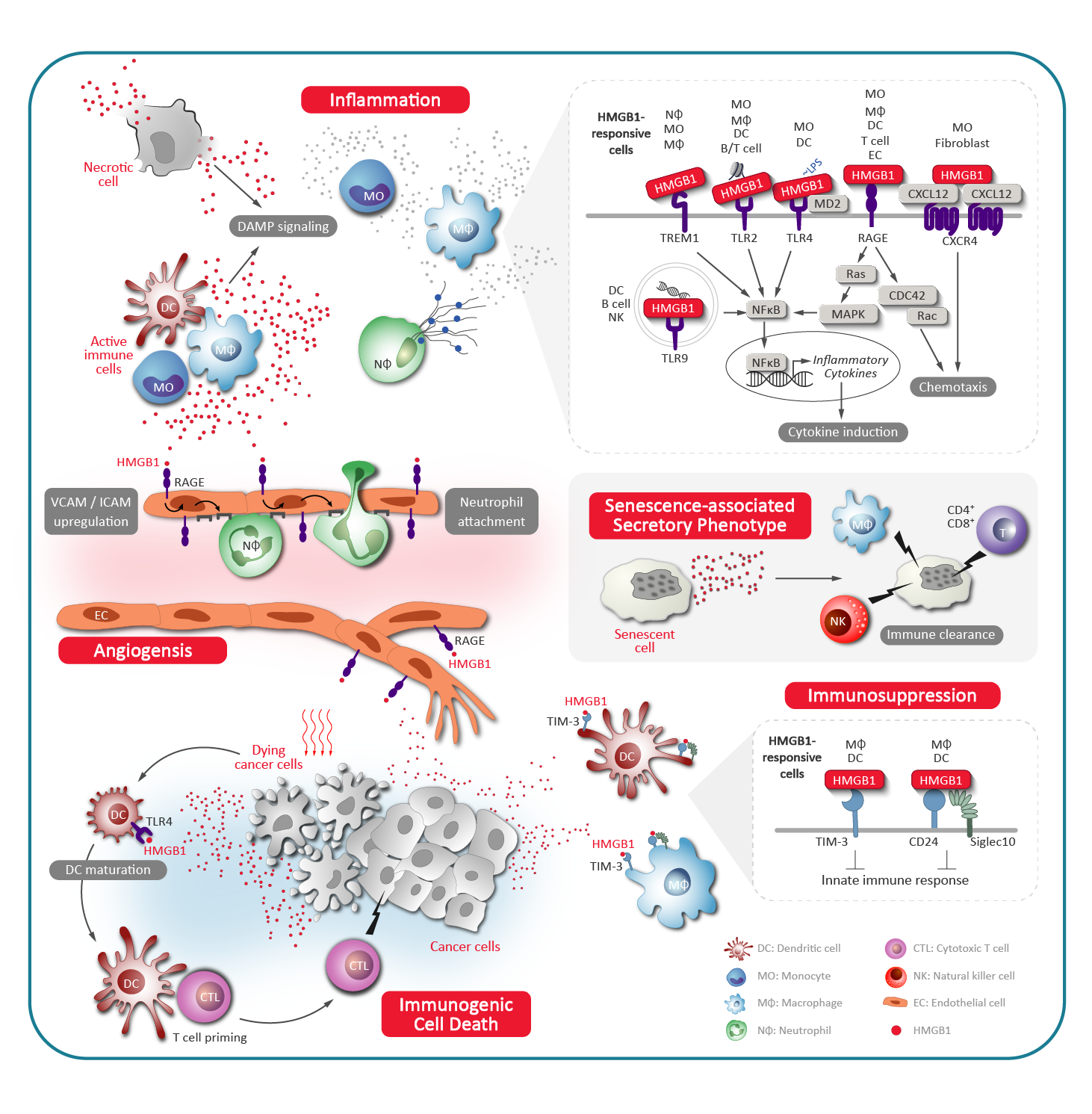
HMGB1 in inflammation
Neutrophils are the first leukocytes recruited to the site of inflammation for destroying pathogens. HMGB1 is required for the recruitment and the defense function of neutrophils.
- HMGB1 promotes neutrophil recruitment
- HMGB1 induces NETosis
- HMGB1 induces production of inflammatory cytokines
- HMGB1 triggers pyroptosis

HMGB1 in TME (tumor microenvironment)
It has dual roles in tumor microenvironment (TME). During tumor development, HMGB1 acts as a pro-tumoral protein by promoting tumor growth, angiogenesis, immunosuppression, invasion and metastasis. However, HMGB1 also plays an anti-tumoral role by mediating immunogenic cell death (ICD) during chemoradiotherapy and enhance anti-tumor immunity. HMGB1 provides potentially therapeutic strategy for cancer chemoradiotherapy and immunotherapy.
Detecting exosomal HMGB1 for ICD research
Kim et al. used this ELISA kit to measure the exosomal HMGB1 levels released from non-irradiated and gamma-irradiated melanoma cancer cells and demonstrated that exosomal HMGB1 stimulates immunogenic cell death (ICD).
HMGB1, a biomarker and therapeutic target in COVID-19
HMGB1, a biomarker for severe COVID-19
HMGB1 promotes release of pro-inflammatory cytokines including TNF, IL-1 and IL-6. Chen et al. reported that elevated serum HMGB1 was associated with high mortality and lung cytokine storm in COVID-19 patients. Their results suggest HMGB1 is a biomarker for severe COVID-19. Comprehensive HMGB1 ELISA Kits
HMGB1, a therapeutic target in COVID-19
HMGB1 contributes to lung cytokine storm and is considered as a potential target for the treatment of COVID-19. Recently, Chen et al. and Wei et al. reported a novel role of HMGB1 in ACE2 expression and viral entry. Chen et al. found that HMGB1 induces the expression of SARS-CoV-2 entry receptor ACE2 in lung epithelial cells. This result indicates that targeting HMGB1 shows benefits of preventing both cytokine storm and viral entry.
Si necesitas más información sobre HMGB1 o como Arigo puede ayudar en tu investigación, pregúntanos:





Leave a reply